views
How many years does it take to become a doctor?
It can take around 10–15 years after high school. After you graduate from high school, you’ll need to earn a degree from a 4-year college before you can apply to medical school. You’ll study in medical school for another 4 years, and then move on to post-medical school training called "residency" for a few years before being eligible to take the United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) which you must pass to practice medicine without restriction. It may seem like a long time, but your experience will help you provide the best care and meet other people in your field. Medical schools will accept any major as long as you complete the prerequisite courses so do not limit yourself to a pre-medical or hard science program. In the United States, you may choose to get an allopathic (MD) or osteopathic (DO) medical degree. MD programs are more competitive than DO programs, with higher admission requirements and lower acceptance rates. However, both degrees provide similar medical education and training. The difference between these two programs are as follows: MD programs emphasize traditional, science-based medical education for treating illness and disease with medications, surgeries, and other conventional therapies. DO programs also provide science-based medical education, but focus on the musculoskeletal system's impact on overall health and well-being, taking a more holistic approach. DOs may also use osteopathic manipulative treatment (OMT), a form of hands-on therapy, in their treatment plans.
What courses should I take before med school?
Complete your prerequisite courses during undergraduate. To become a doctor, you will need to complete coursework in biology, general chemistry (including organic chemistry), and physics. Note that most medical schools do not accept AP credits. You'll need to retake any AP science courses in college to receive a grade that reflects your understanding of the subject. Until you complete the necessary prerequisites and earned your Bachelor's Degree, you cannot apply to medical school. Some of the prerequisite classes that will be helpful to you as a future doctor include: General Biology (two semesters): Medical professionals need a solid understanding of general biology to understand how the human body works, and how to diagnose and treat diseases. Without a strong grasp of basic biological concepts, it would be difficult for doctors to provide effective care to their patients. General Chemistry (two semesters): Doctors need to know general chemistry because it is essential to understanding how drugs and other substances interact with the body. This knowledge is necessary for prescribing medications, interpreting laboratory test results, and understanding the basic biochemical processes that occur in the body. Inorganic Chemistry (two semesters): Doctors need to know inorganic chemistry because it is the basis for understanding how drugs work and how the body interacts with them. Inorganic chemistry also helps doctors understand how nutrients and other substances are transported throughout the body. Physics (two semesters): Doctors need to know physics because it helps them understand how the body works at a physical level, including the principles of motion, energy, and force. This understanding is important in diagnosing and treating medical conditions, interpreting diagnostic tests, and designing treatment plans.

Include a few classes in psychology or sociology. Go through the list of available courses at your school and try to add a couple behavioral sciences to your schedule. Taking these courses helps you learn more about how people think and behave, which can help you offer the best treatment for whatever issue they’re dealing with. Course requirements depend on which medical school you want to go to. Always check the websites for the schools you’re interested in to see what courses you need to take.
What degree do I need before I go to med school?

Earn a bachelor’s degree in science before applying. You can go to any 4-year school to earn your bachelor’s degree. While many med schools will accept most degree programs, you’ll have better prepared for medical school if you choose a science-related field, such as biology or chemistry, since it will help you more with the courses in medical school. You should also be taking hard courses since it will impress the admission officer and increase your chance of being accepted. For example, a B in Calculus is better than an A in an easy course such as Art or Communications.
What extracurriculars can I do to help me get into med school?

Look for medical volunteer opportunities. You can start volunteering once you’re in high school so you can get an early start on your career. Visit the website for your local hospital or clinic and search for “Volunteer Opportunities” to see if they have any available positions. Some things you can do to volunteer include greeting patients, escorting patients through the clinic, and answering phones. Otherwise, talk to your school’s guidance or career counselor to see if they can help you make connections. If your school has a career day, look for representatives from local hospitals or clinics and ask what volunteer positions are available.
How do I apply to medical school?
Take the MCAT exam and submit your scores to potential schools. The Medical College Admission Test (MCAT) is a standardized test that’s required for your med school application. The test is multiple-choice and is split into 4 sections: Biological and Biochemical Foundations; Chemical and Physical Foundations; Psychological, Social, and Biological Foundations; and Critical Analysis and Reasoning. Schedule the exam within 3 years of applying to med school to ensure they accept your scores. Look for study guides online or at bookstores and try to set aside some time every day to review the information before the test. If you receive testing accommodations for a disability, visit the AAMC website to learn how to register for accommodations and follow the instructions.
Fill out the application for the school you want to go to. Research a few potential medical schools that you want to attend and check if you meet the application requirements. Fill out the application online with your information, transcripts, and any essays that they ask you to write. Be sure to submit your application before the deadline listed on the site to ensure that you qualify for the coming academic year. Start your application in the spring of your junior year of college if you plan on going to med school right after graduation. Many med school applications have a one-time fee that varies between institutions. You may also need letters of recommendation from professors or advisors.

Interview with someone from the school to see if you’re a good fit. After your application gets accepted, you’ll typically have to do an interview with a faculty member in-person or over a video call. The interviewer will ask you things like why you want to be a doctor and why you want to attend their school. Answer all the questions honestly as best as you can for the best chances of getting accepted. No matter how the interview went, send a follow-up email thanking the person for their time and consideration. Try running a mock interview with a friend or mentor so you can get used to answering the questions. Just make sure you don’t memorize responses, or else it will seem like you’re too rehearsed.
What do I do during medical school?
Take pre-clinic classes for the first 2 years. When you first start medical school, you’ll work mostly in a classroom so you can familiarize yourself with basic medical concepts. You’ll learn about body functions, diseases, and treatments. You’ll also cover basic doctoring skills, like taking medical histories and communicating with patients.

Work with patients during clinicals during your last 2 years. As you get more knowledgeable, your professors will let you interact and work with patients so you get hands-on experience making rounds and treating others. Listen carefully to the supervising doctor and follow their instructions so you can continue learning and improving. Some schools might have a more integrated curriculum where you start doing clinicals interspersed with your classes.
Take the first 2 parts of the USMLE during school to get a general license. The United States Medical Licensing Exam, or USMLE, is a required 3-step test for all medical students. Each step of the exam is multiple-choice covering basic medical information and takes around 8 hours to complete. Apply to take the first and second steps of the exam while you’re still enrolled at your med school, but you can’t take the final step until you’re working on a residency. Scores range from 1 to 300, where 300 is the best. Typical median scores for step 1 and 2 of the exam are around 232 and 245 respectively. You can retake each step of the USMLE up to 6 times.
How do I choose a medical specialty?
Pick something that you’ve enjoyed doing in med school. During your final years of medical school, you get to choose what area of medicine you want to focus on. Think hard about what you’ve liked learning about and if those paths are what you want to pursue in your career. If you aren’t sure what you want to do, talk to an advisor or counselor at your school to help you find the field that you’re best suited for. For example, go into pediatrics or family medicine if you want to work with younger patients. As another example, if you’ve been really interested in bones and joints during class, you may go into orthopedics instead. Some of the most competitive medical specialties include radiology, orthopedic surgery, integrated plastic surgery, and neurological surgery.

Decide if you want to be in a hospital or private practice. When you work at a hospital, you’ll do more work with teams and have administrators handle all the paperwork you need. However, hospitals can be more stressful since your hours can change depending on the week and you’ll work with a large variety of patients. If you want more control of your hours and want to establish better connections with the people you’re treating, choose a private clinic instead. If you enjoyed making rounds during med school, fields such as general surgery or internal medicine at a hospital may be a good choice for you. Consider fields like psychiatry, dermatology, or pathology if you want to have more control over the patients you see and want to work in a specialized clinic.
What should I expect during residency?

You’ll gain experience working in your field under supervision. After choosing a specialty you want to practice, apply for a residency in a clinic or medical practice. Once you’re accepted, you can interact and help with patients while more experienced doctors watch over you. That way, you can learn even more about your field's specialized services and work with patients outside of medical school.

Plan on being a resident for 3–7 years. Residency lengths all depend on the difficulty of the field that you chose as your specialty. If you’re only working in general medicine, then you usually get by with only 3 years. However, more difficult fields, such as neurology and surgery, may take 5–7 years to complete fully.
How do I get certified to practice medicine?
Check the license requirements for your state. Each state has its own requirements before you can apply for a medical license. Some states require a certain number of years in residency while others may have restrictions for how many times you take the USMLE. You will need a license for each state where you want to practice. You can find state-specific requirements here: https://www.fsmb.org/step-3/state-licensure/.
Take a board certification exam for your medical specialty. Contact your state’s licensure department as you get closer to the end of your residency to find out how to apply to the board exam. Most board exams are written tests, but some specialties may require an oral exam too. Once you pass your boards, you can then practice anywhere within the state. Average board exams can cost around $2,000 USD.
How much is a doctor’s salary?
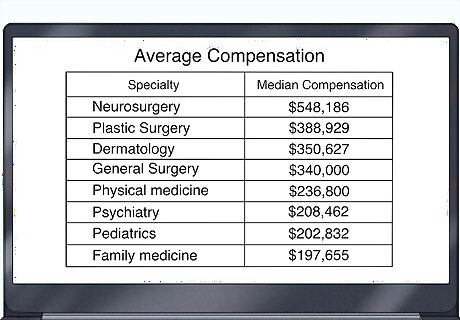
You can earn around $200,000 USD a year as a general doctor. If you only practice general medicine, you’ll usually average around this much every year. If you practice a more specific field of medicine, you’ll most likely earn more money depending on the difficulty of what you’re doing. For example, you could earn an average of $350,000 USD a year if you’re a dermatologist or up to $550,000 USD if you’re a neurosurgeon.















Comments
0 comment