
views
For personalized advice, take our Erectile Dysfunction Quiz to find out if you have ED and get access to quick and easy treatment options.
Making Lifestyle Changes

Improve your nutrition. Certain foods, such as those that are fatty, fried, sugary, and processed, can result in decreased blood flow throughout your body and can contribute to a vascular form of erectile dysfunction. Increase your intake of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and heart-healthy fats to improve your blood circulation and increase the amount of time you’re able to maintain an erection. A diet high in animal fat will put pressure on your cardiovascular system, potentially damaging your blood flow. Try to limit the amount of meat and cheese you eat. Include more sources of potassium, such as bananas, garlic, onions, and almonds. Mix 1 teaspoon (3 g) of Indian ginseng powder into a glass of milk and drink it before bed to help increase your endurance.
Exercise on a regular basis. There is evidence that suggests that a sedentary lifestyle can be a factor in erectile dysfunction. Aerobic exercises, such as running and swimming, can help prevent ED. The exercise can help improve blood flow and circulation, naturally help lower high blood pressure and cholesterol, and can even help improve hormonal balance and drive weight loss – all of which are factors that can help you improve ED and maintain an erection. Be wary of exercise that puts particular pressure on your perineum (the area between your scrotum and penis). If you like going for long bike rides, be sure you have a bike that fits. Opt for a padded seat, wear some padded shorts, and be sure to stand up on the pedals regularly.

Watch your weight. Eating a healthy diet and getting plenty of exercise will improve your overall health and help increase your blood flow. Maintaining a healthy weight by combining a healthy diet with exercise will also help you lower your risk of type diabetes, which can contribute to ED. If you are overweight you may have a heightened risk of high blood pressure and high cholesterol, both of which can damage blood vessels. Having good blood flow is important for maintaining an erection. If you’re overweight, losing weight can help you to tackle erectile dysfunction.

Stop smoking cigarettes and tobacco products. Smoking can constrict your blood vessels and affect blood flow, which can lead to problems with maintaining an erection. Stop smoking as soon as possible, and practice one or more smoking cessation programs that can help you kick your habit indefinitely. Studies have shown that smokers are much more likely to suffer from erectile dysfunction than non-smokers.
Drink alcohol only in moderation. Chronic heavy drinking can interfere with normal bodily functions, including your ability to maintain an erection. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine the amount of alcohol you should or should not be consuming regularly based on your health history. It is not uncommon for a man to be unable to maintain an erection if he has been drinking heavily immediately beforehand.

Treat and manage stress. Psychological stress can increase your body’s levels of cortisol and adrenaline, leading to hormonal imbalance and the constriction of blood vessels. If you frequently suffer from stress, look for ways to eliminate reduce stresses from your life, or find new, healthy ways to manage stress. Practice deep breathing and yoga, listen to music, or set aside more time in which to enjoy your favourite activities.
Working With Your Partner

Talk to your partner. Communicate openly to your partner about your difficulty maintaining an erection. Couples who are unable to talk openly to each other sometimes find it harder to be sexually intimate. If there is no communication, each partner may blame themselves. If you are both uncomfortable talking about it counselling may help. In some cases, your partner may have ideas or suggestions about how he or she can help you maintain your erection in the bedroom. Getting to really know your partner will help you become more intimate and feel more comfortable.
Be intimate in new ways. If your sex is focused just on penetration and climax, you may feel under more pressure to quickly get and maintain an erection, which can make this harder to do. Try to find new and more varied ways to be intimate with your partner that are not just about sprinting to the finish line. Take time with each other, such as taking a bath or shower together or massaging each other. You can also try practicing different sexual positions to enhance blood flow. Being on top or standing up while engaging in sexual activity can increase your blood flow and help you maintain an erection.

Consider counselling. If you or your doctor suspect your problems with maintaining an erection are psychological, consider the possibility of undergoing counselling. A professional, experienced psychologist may be able to help reverse your problems with ED. Problems with maintaining erections are not normally psychological. Emotional causes are more common in younger men and physical causes in older men. If you have erections in the morning or at night, it is likely that your difficulties maintaining an erection for intercourse are not physical.
Treating Erectile Dysfunction Medically
Visit your doctor. If you have tried making changes to your lifestyle, and you are still struggling to maintain an erection, make an appointment with your healthcare provider. ED can be caused by type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, certain prescription medications, stress, and even excess body weight. Your doctor will check your blood flow circulation, examine your penis and rectum, examine your nervous system, and ask you questions about your medical history, such as how long you have had trouble maintaining an erection. Your doctor will rate your cardiovascular risk factors as mild, moderate, severe, and make sure that your heart is healthy enough for sex. Your doctor can help recommend the proper course of treatment to resolve ED based on your personal health history. For example, if you have low levels of testosterone, your doctor may recommend a testosterone patch. If you are relatively healthy, then your ED may be classified as psychogenic, which means that there is a mental or emotional barrier preventing you from getting and/or maintaining an erection.
Get a blood test to evaluate your testosterone levels. Testosterone naturally peaks in adolescence and young adulthood and drops off as you age. If a blood test reveals that you have low testosterone levels, there's a good chance this could be the culprit behind your erectile dysfunction. Your doctor will likely recommend natural lifestyle changes first, such as losing weight or increasing muscle mass. If your testosterone levels are lower than average for your age, they may prescribe taking supplemental testosterone. If you're experiencing low testosterone levels as a result of aging, remember that this is completely normal. It's not currently advised to take testosterone as a way of addressing this.
Consider oral medication. Your doctor may prescribe you medication that works by increasing the blood flow to your penis, and thus helping you maintain an erection. Medications commonly used to treat ED include Viagra, Cialis, and Levitra. If your doctor prescribes Cialis, your doctor will likely recommend that you take 10 to 20 mg at least 30 minutes before sexual activity. You should not take the medication if you experience severe hyperactivity to the medication or if you are using nitrates, such as nitroglycerin, for chest pain. If your doctor prescribes Levitra, then you will need to take it with or without food 60 minutes before sex. This medication should not be taken with nitrates either.
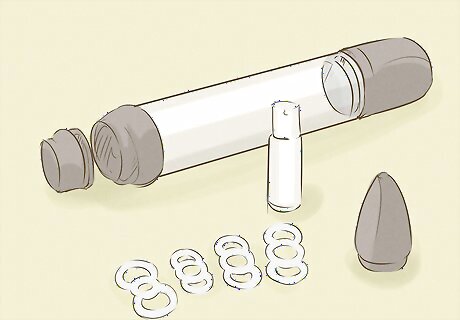
Investigate mechanical aids. You may also ask your doctor about the use of mechanical aids to help you achieve and maintain an erection. Some men use vacuum devices and constriction rings to aid erections. The vacuum is placed over the penis and pumps out air, drawing blood to the penis and causing an erection. This is maintained by placing a band or ring at the base of the penis, that keep it erect for up to thirty minutes. This can, however, be a uncomfortable and awkward way to treat ED.
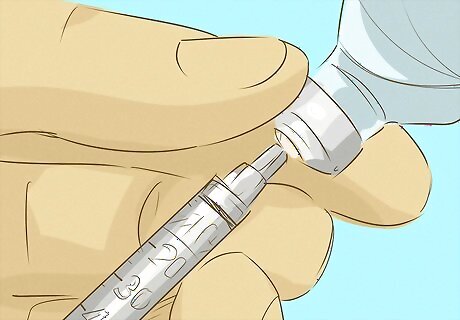
Use penile injection therapy. An alternative method that you may be advised on by a doctor is penile injection therapy. For this you will be trained by the doctor how to inject your penis with medicine that relaxes the blood vessels and promotes the blood flow that causes an erection. This treatment has been shown to be effective at treating a range of issues both physical and psychological. Potential side effects include scarring, and the risk of sustained and painful erections if improperly dosed. You may experience high blood pressure and dizziness as a result of injection therapy.
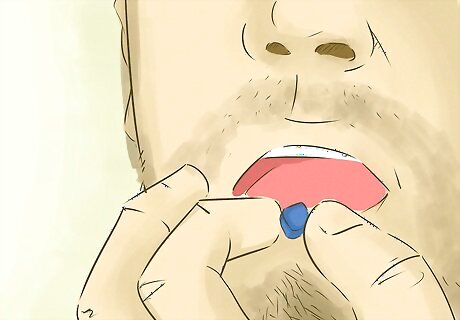
Ask about transurethral pharmacotherapy. Your doctor may suggest you try this treatment, which involves placing a suppository into the urethra. The suppository contains alprostadil, which is then absorbed into the blood stream, relaxing blood vessels and improving blood flow into the penis. This treatment is thought to be less effective than the vacuum devices, or injection therapy.
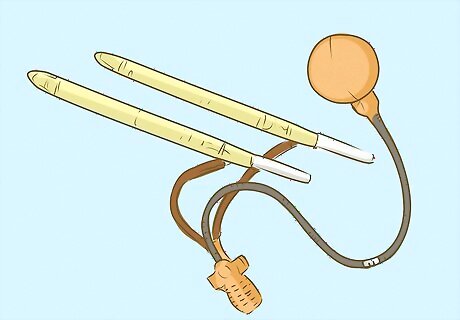
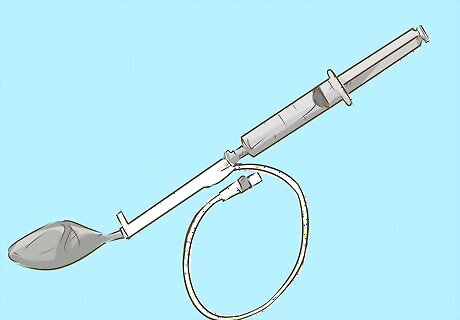
Evaluate surgical options. If the other treatments have not proven successful, your doctor may recommend a surgical procedure that will involve an inflatable penile prosthesis being implanted into your penis. Typically a pair of inflatable cylinders are inserted into the penis, which can be pumped up and deflated using a connected device that is inserted into the scrotal sac. The prosthesis does not change the sensation on the skin, or effect the man’s ability to orgasm and ejaculate. The surgery involves two small incisions and is not noticeable after healing.



















Comments
0 comment