
views
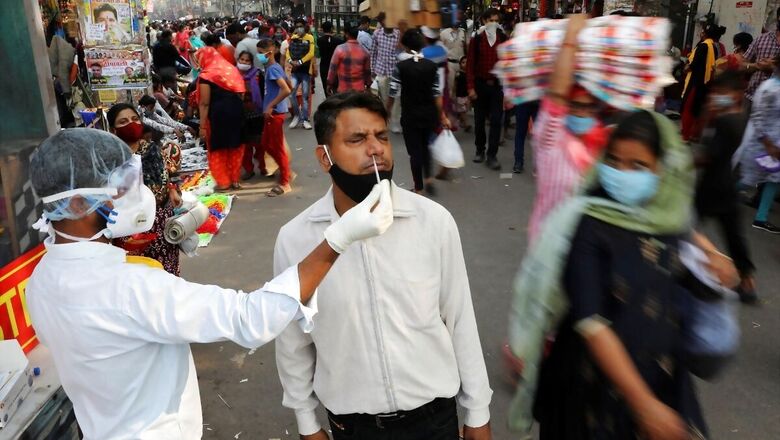
Delhi Health Minister Satyendar Jain said on Tuesday 56.13 per cent of those covered under the latest serological survey in the city in January have developed antibodies against coronavirus. The minister also said Delhi was "moving towards herd immunity, but only experts will be able to give a clear picture".
The fifth sero survey — the largest in the country so far — was conducted from January 15 to January 23, he said. At 62.18 percent, Southwest Delhi district reported maximum seroprevalence. North Delhi at 49.09 percent recorded the lowest, Jain said.
"A new, better technology was used during the survey. Samples were collected from every ward. In all, 28,000 samples were taken," a senior official said. The minister said the number of cases, fatalities and hospital admissions have declined significantly, but insisted that people should continue use masks for a few more months and maintain "COVID-19-approriate behavior".
Jain said three major changes were incorporated during the latest survey. "We increased the sample size. Samples were collected on the basis of socio-economic conditions. A new, more sensitive kit was used and the testing was conducted at Institute of Liver and Biliary Sciences," he said.
The minister also informed that frontline workers will start getting COVID-19 vaccine jabs this week. Nearly six lakh frontline workers, including government school teachers, MCD employees, police personnel, ASHA and ANM workers, are expected to be administered the vaccine.
The findings are helpful to assess the rate of spread of the disease but need to be taken with caveats, said immunologist Satish Devadas. “Even if the sample size is relatively small, it must be taken to account. However, the conclusions on herd immunity have to be taken with a pinch of salt,” Devadas, a scientist with the Institute of Life Sciences in Odisha, told PTI.
Other scientists also advise abundant caution. Though the results suggest the possibility that herd immunity may break the chain of COVID-19 transmission and the findings are insightful to get an idea of the community spread of the coronavirus in the city, several experts said the dangers may be far from over.
The number of daily reported COVID-19 cases has been on a steady decline since the city’s highest single-day spike of 8,593 cases on November 11. On Monday, the city reported 121 fresh cases and three deaths, the lowest in 10 months. Herd immunity occurs when a significantly large number of people ina community become immune to a contagious disease after recovering from infection, thereby curbing its spread across the population.
Experts noted that it is not known what the number of recovered individuals need to be in a community to break the chain of viral transmission with herd immunity. “Our best bet is still in the 60-70 per cent range but this is based on theory, and not on specific information we have about duration of immune protection following infection,” epidemiologist Ramanan Laxminarayan said.
Laxminarayan, founder and director of the Center for Disease Dynamics, Economics & Policy (CDDEP) in the US, said many pockets within urban India may have already reached this threshold. However, it remains unclear if even herd immunity with a 60-70 per cent seropositivity in a population could still prevent a subsequent wave of COVID-19.
Scientists cited the example of the Brazilian city of Manaus, where immunity against the infection may have begun to wane already. A study of blood donors in the city, published in the journal Science, indicated that about 76 per cent of the population may have been infected with SARS-CoV-2 by October 2020 — an infection rate that would have been above the theoretical herd immunity threshold. Coinciding with this, COVID-19 hospitalisations in the city peaked in late April and also remained stable and “fairly low” from May to November, noted a commentary published in The Lancet journal on Thursday.
While some experts noted that this may have been due to the population attaining herd immunity, the scientists, including those from Universidade de Sao Paulo in Brazil, said a sudden abrupt increase in the number of COVID-19 hospital admissions in Manaus this month has been unexpected and a “cause for concern”. One of the reasons cited by the scientists in the commentary was that immunity against infection observed in the Manaus population might have begun to wane by December 2020 after initial exposure to the coronavirus. The scientists also highlighted the possibility of new lineages of the coronavirus driving a resurgence of cases in places with high seropositivity if these virus variants have increased transmissibility compared with pre-existing circulating strains.
“If resurgence in Manaus is due to waning of protective immunity, then similar resurgence scenarios should be expected in other locations,” the scientists wrote in the commentary. Immunologist Satyajit Rath believes there is a possibility of a similar situation in cities across the world, including Delhi.
“High rates of infection and seropositivity in the large Brazilian city of Manaus initially seemed to indicate effective ‘herd immunity’, but then case numbers began going up again in Manaus,” said Rath, who is affiliated with New Delhi’s National Institute of Immunology. “There is some indication that this may be accompanied by declining seropositivity because antibody responses may not be well sustained over time in all affected people. That would make them re-susceptible,” he added.
Rath said the infection and seropositivity patterns in the population are extremely variable for the novel coronavirus, and “a hundred samples per municipal ward in Delhi may not have captured this variation and may therefore be overestimating overall seropositivity”. “Post lockdown the restrictions on movement have decreased and hence communities cannot remain in isolation. Thus a general comment about herd immunity or community immunity is unrealistic at this juncture,” added immunologist Vineeta Bal, affiliated with the Indian Institute of Science Education and Research, Pune. Recent studies, including those from Rockefeller University in the US, have indicated that a declining count of antibodies in recovered individuals may still not suggest a risk of reinfection.
Michel C Nussenzweig, lead authors of one of these studies, noted that instead of the body producing antibodies all the time after recovering from the virus, the immune system creates memory B cells which recognise the coronavirus, and quickly unleash a new round of antibodies when they encounter it a second time. This study, published in the journal Nature, also noted that residual viral particles hiding within gut tissues could be driving the evolution of memory B cells in a way that may potentially train it to tackle emerging variants of the virus.
With reliable estimates not available on the percentage of people that need to be immune-protected in order to halt the spread of the virus definitively, Rath said vaccination may be the way forward. Bal agreed.
Since the number of vaccine doses currently available in the country is limited, and with the immunisation drive progressing very slowly, she believes the seroprevalence data does not provide any useful information for vaccination. Research has also shown that recovered and vaccinated individuals may also not completely break the transmission of the virus.
Experts, including Anthony Fauci, chief medical advisor to US President Joe Biden, haveadvised vaccinated and recovered individuals to continue wearing masks.
Read all the Latest News, Breaking News and Coronavirus News here












Comments
0 comment