views
c
2
=
a
2
+
b
2
−
2
a
b
cos
C
{\displaystyle c^{2}=a^{2}+b^{2}-2ab\cos {C}}
.
Finding a Missing Side Length
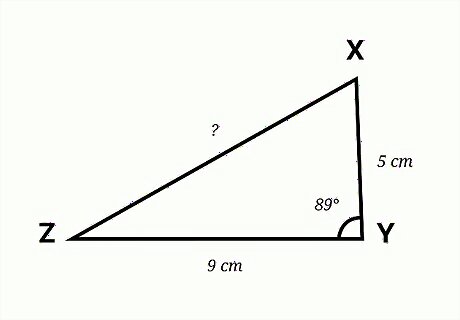
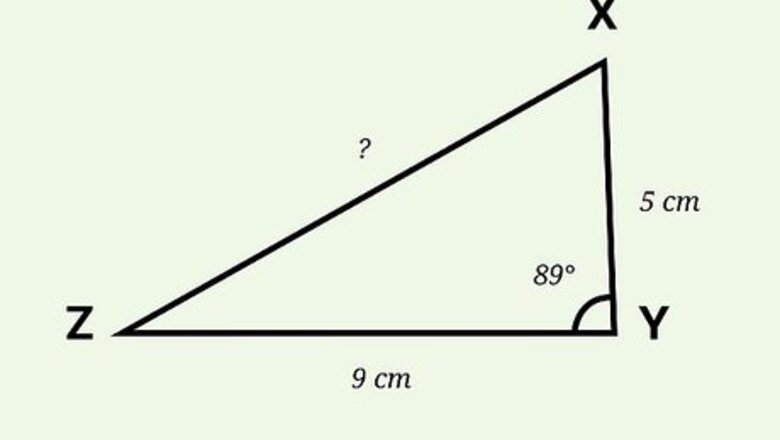
Assess what values you know. To find the missing side length of a triangle, you need to know the lengths of the other two sides, as well as the size of the angle between them. For example, you might have triangle XYZ. Side YX is 5 cm long. Side YZ is 9 cm long. Angle Y is 89 degrees. How long is side XZ?
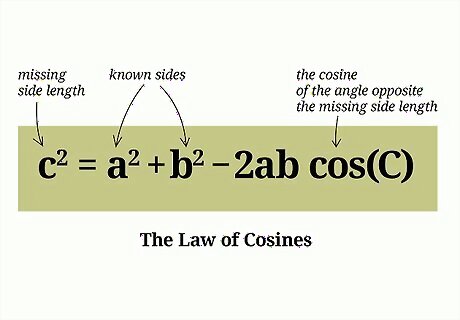
Set up the formula for the Cosine Rule. This is also called the law of cosines. The formula is c 2 = a 2 + b 2 − 2 a b cos C {\displaystyle c^{2}=a^{2}+b^{2}-2ab\cos {C}} c^{{2}}=a^{{2}}+b^{{2}}-2ab\cos {C}. In this formula, c {\displaystyle c} c equals the missing side length, and cos C {\displaystyle \cos {C}} \cos {C} equals the cosine of the angle opposite the missing side length. The variables a {\displaystyle a} a and b {\displaystyle b} b are the lengths of the two known sides.
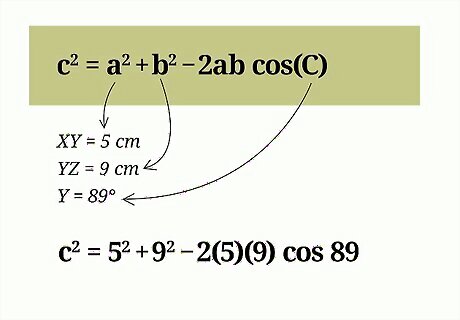
Plug the known values into the formula. The variables a {\displaystyle a} a and b {\displaystyle b} b are the two known side lengths. The variable C {\displaystyle C} C is the known angle, which should be the angle between a {\displaystyle a} a and b {\displaystyle b} b. For example, since the length of side XZ is missing, this side length will stand for c {\displaystyle c} c in the formula. Since sides YX and YZ are known, these two side lengths will be a {\displaystyle a} a and b {\displaystyle b} b. It doesn’t matter which side is which variable. The variable C {\displaystyle C} C is angle Y. So, your formula should look like this: c 2 = 5 2 + 9 2 − 2 ( 5 ) ( 9 ) cos 89 {\displaystyle c^{2}=5^{2}+9^{2}-2(5)(9)\cos {89}} c^{{2}}=5^{{2}}+9^{{2}}-2(5)(9)\cos {89}.
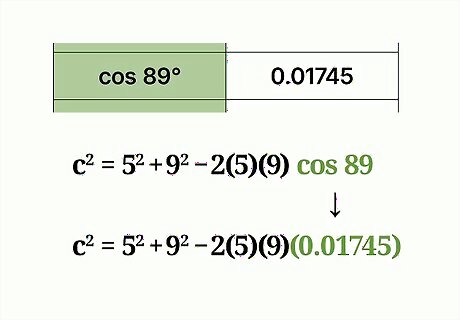
Find the cosine of the known angle. Do this using a calculator’s cosine function. Simply type in the angle measurement, then hit the C O S {\displaystyle COS} COS button. If you don't have a scientific calculator, you can find a cosine table online. You can also simply type in "cosine x degrees" into Google, (substituting the angle for x), and the search engine will give back the calculation. For example, the cosine of 89 is about 0.01745. So, plug this value into your formula: c 2 = 5 2 + 9 2 − 2 ( 5 ) ( 9 ) ( 0.01745 ) {\displaystyle c^{2}=5^{2}+9^{2}-2(5)(9)(0.01745)} c^{{2}}=5^{{2}}+9^{{2}}-2(5)(9)(0.01745).
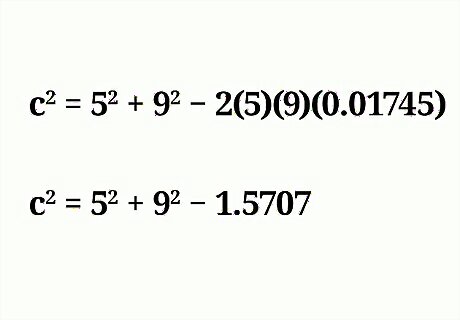
Complete the necessary multiplication. You are multiplying 2 a b {\displaystyle 2ab} 2ab by the known angle’s cosine. For example: c 2 = 5 2 + 9 2 − 2 ( 5 ) ( 9 ) ( 0.01745 ) {\displaystyle c^{2}=5^{2}+9^{2}-2(5)(9)(0.01745)} c^{{2}}=5^{{2}}+9^{{2}}-2(5)(9)(0.01745) c 2 = 5 2 + 9 2 − 1.5707 {\displaystyle c^{2}=5^{2}+9^{2}-1.5707} c^{{2}}=5^{{2}}+9^{{2}}-1.5707
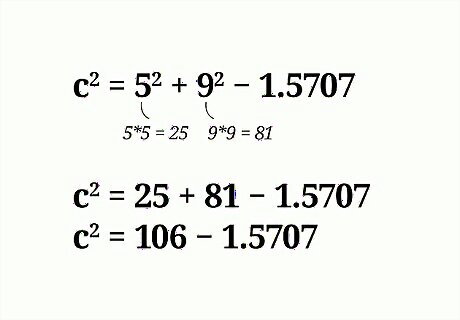
Add the squares of the known sides. Remember that when you square a number, you multiply it by itself. Square the two numbers first, then add them. For example: c 2 = 5 2 + 9 2 − 1.5707 {\displaystyle c^{2}=5^{2}+9^{2}-1.5707} c^{{2}}=5^{{2}}+9^{{2}}-1.5707 c 2 = 25 + 81 − 1.5707 {\displaystyle c^{2}=25+81-1.5707} c^{{2}}=25+81-1.5707 c 2 = 106 − 1.5707 {\displaystyle c^{2}=106-1.5707} c^{{2}}=106-1.5707
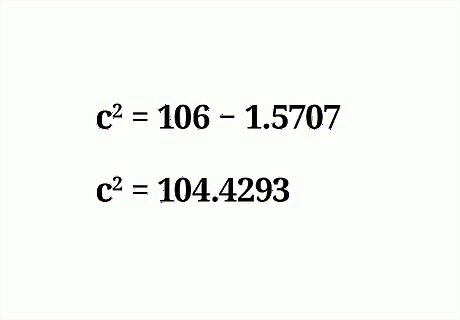
Subtract the two values. This will give you the value of c 2 {\displaystyle c^{2}} c^{{2}}. For example: c 2 = 106 − 1.5707 {\displaystyle c^{2}=106-1.5707} c^{{2}}=106-1.5707 c 2 = 104.4293 {\displaystyle c^{2}=104.4293} c^{{2}}=104.4293
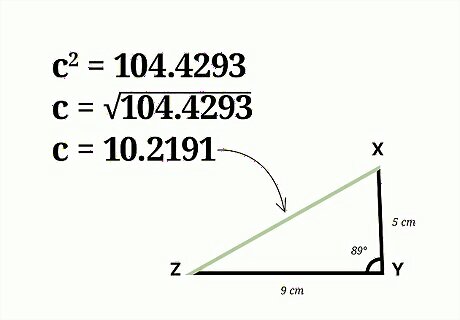
Take the square root of the difference. You will likely want to use a calculator for this step, because the number you are finding the square root of will have many decimal places. The square root is equal to the length of the missing side of the triangle. For example: c 2 = 104.4293 {\displaystyle c^{2}=104.4293} c^{{2}}=104.4293 c 2 = 104.4293 {\displaystyle {\sqrt {c^{2}}}={\sqrt {104.4293}}} {\sqrt {c^{{2}}}}={\sqrt {104.4293}} c = 10.2191 {\displaystyle c=10.2191} c=10.2191So, the missing side length, c {\displaystyle c} c, is 10.2191 cm long.
Finding a Missing Angle
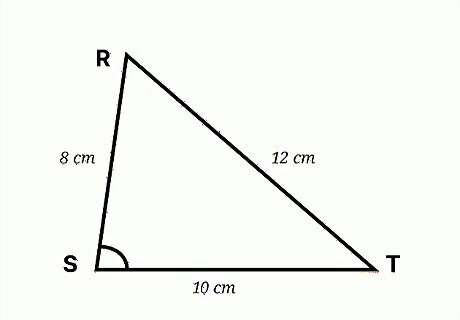
Assess what values you know. To find the missing angle of a triangle using the cosine rule, you need to know the length of all three sides of the triangle. For example, you might have triangle RST. Side SR is 8 cm long. Side ST is 10 cm long. Side RT is 12 cm long. What is the measurement of angle S?
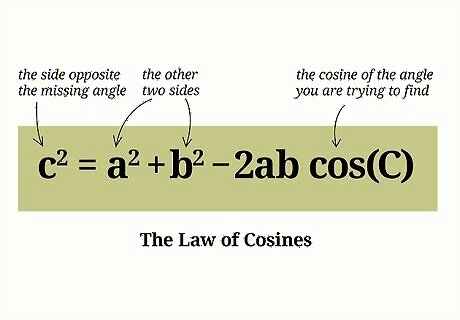
Set up the formula for the Cosine Rule. The formula is c 2 = a 2 + b 2 − 2 a b cos C {\displaystyle c^{2}=a^{2}+b^{2}-2ab\cos {C}} c^{{2}}=a^{{2}}+b^{{2}}-2ab\cos {C}. In this formula, cos C {\displaystyle \cos {C}} \cos {C} equals the cosine of the angle you are trying to find. The variable c {\displaystyle c} c equals the side opposite the missing angle. The variables a {\displaystyle a} a and b {\displaystyle b} b are the lengths of the other two sides.
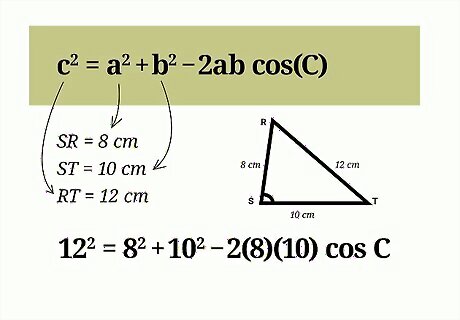
Determine the values of a {\displaystyle a} a, b {\displaystyle b} b, and c {\displaystyle c} c. Plug these values into the formula. For example, since side RT is opposite the missing angle, angle S, side RT will equal c {\displaystyle c} c in the formula. The other two side lengths will be a {\displaystyle a} a and b {\displaystyle b} b. It doesn’t matter which side is which variable. So, your formula should look like this: 12 2 = 8 2 + 10 2 − 2 ( 8 ) ( 10 ) cos C {\displaystyle 12^{2}=8^{2}+10^{2}-2(8)(10)\cos {C}} 12^{{2}}=8^{{2}}+10^{{2}}-2(8)(10)\cos {C}.
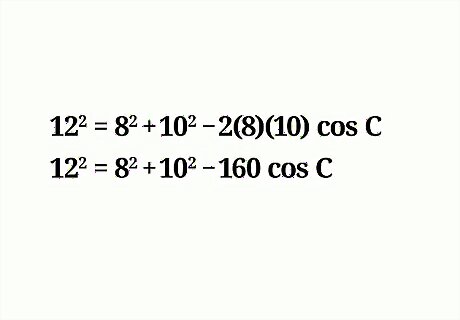
Complete the necessary multiplication. You are multiplying 2 a b {\displaystyle 2ab} 2ab times the cosine of the missing angle, which you don’t know yet. So, the variable should remain. For example, 12 2 = 8 2 + 10 2 − 160 cos C {\displaystyle 12^{2}=8^{2}+10^{2}-160\cos {C}} 12^{{2}}=8^{{2}}+10^{{2}}-160\cos {C}.

Find the square of c {\displaystyle c} c. Remember that to square a number, you multiply the number by itself. For example, 144 = 8 2 + 10 2 − 160 cos C {\displaystyle 144=8^{2}+10^{2}-160\cos {C}} 144=8^{{2}}+10^{{2}}-160\cos {C}
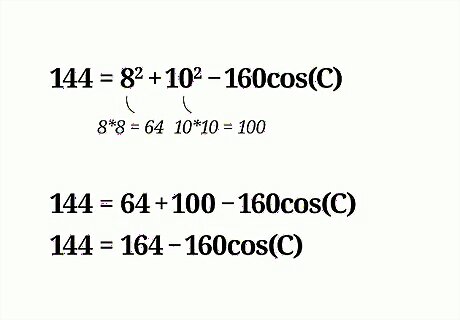
Add the squares of a {\displaystyle a} a and b {\displaystyle b} b. Make sure you square each number first, and then add them together. For example: 144 = 64 + 100 − 160 cos C {\displaystyle 144=64+100-160\cos {C}} 144=64+100-160\cos {C} 144 = 164 − 160 cos C {\displaystyle 144=164-160\cos {C}} 144=164-160\cos {C}
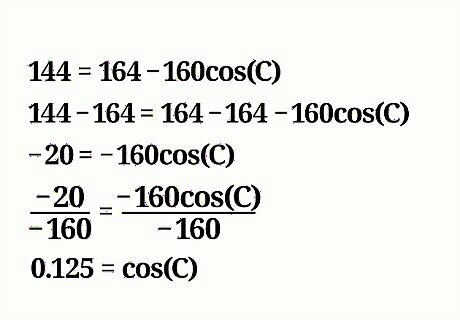
Isolate the cosine of the missing angle. To do this, subtract the sum of a 2 {\displaystyle a^{2}} a^{{2}} and b 2 {\displaystyle b^{2}} b^{{2}} from both sides of the equation. Then, divide each side of the equation by the coefficient of the missing angle’s cosine. For example, to isolate the cosine of the missing angle, subtract 164 from both sides of the equation, then divide each side by -160: 144 − 164 = 164 − 164 − 160 cos C {\displaystyle 144-164=164-164-160\cos {C}} 144-164=164-164-160\cos {C} − 20 = − 160 cos C {\displaystyle -20=-160\cos {C}} -20=-160\cos {C} − 20 − 160 = − 160 cos C − 160 {\displaystyle {\frac {-20}{-160}}={\frac {-160\cos {C}}{-160}}} {\frac {-20}{-160}}={\frac {-160\cos {C}}{-160}} 0.125 = cos C {\displaystyle 0.125=\cos {C}} 0.125=\cos {C}
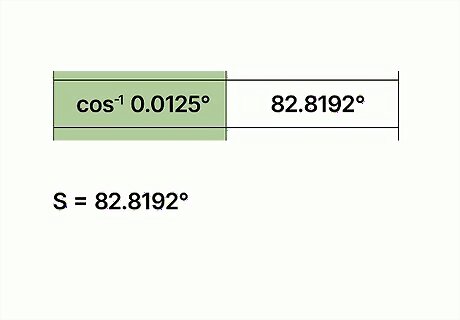
Find the inverse cosine. This will give you the measurement of the missing angle. On a calculator, the inverse cosine key is denoted by C O S − 1 {\displaystyle COS^{-1}} COS^{{-1}}. For example, the inverse cosine of .0125 is 82.8192. So, the missing angle, angle S, is 82.8192 degrees.
Solving Sample Problems
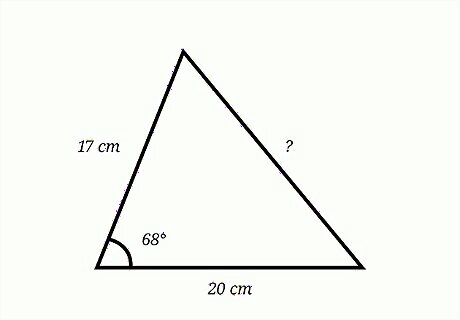
Find the missing side length of a triangle. The two known side lengths are 20 and 17 cm long. The angle between these two sides is 68 degrees. Since you know two side lengths, and the angle between them, you can use the cosine rule. Set up the formula: c 2 = a 2 + b 2 − 2 a b cos C {\displaystyle c^{2}=a^{2}+b^{2}-2ab\cos {C}} c^{{2}}=a^{{2}}+b^{{2}}-2ab\cos {C}. The missing side length is c {\displaystyle c} c. Plug the other values into the formula: c 2 = 20 2 + 17 2 − 2 ( 20 ) ( 17 ) cos 68 {\displaystyle c^{2}=20^{2}+17^{2}-2(20)(17)\cos {68}} c^{{2}}=20^{{2}}+17^{{2}}-2(20)(17)\cos {68}. Use the order of operations to find c 2 {\displaystyle c^{2}} c^{{2}}: c 2 = 20 2 + 17 2 − 2 ( 20 ) ( 17 ) cos 68 {\displaystyle c^{2}=20^{2}+17^{2}-2(20)(17)\cos {68}} c^{{2}}=20^{{2}}+17^{{2}}-2(20)(17)\cos {68} c 2 = 20 2 + 17 2 − 2 ( 20 ) ( 17 ) ( .3746 ) {\displaystyle c^{2}=20^{2}+17^{2}-2(20)(17)(.3746)} c^{{2}}=20^{{2}}+17^{{2}}-2(20)(17)(.3746) c 2 = 20 2 + 17 2 − 254.7325 {\displaystyle c^{2}=20^{2}+17^{2}-254.7325} c^{{2}}=20^{{2}}+17^{{2}}-254.7325 c 2 = 400 + 289 − 254.7325 {\displaystyle c^{2}=400+289-254.7325} c^{{2}}=400+289-254.7325 c 2 = 689 − 254.7325 {\displaystyle c^{2}=689-254.7325} c^{{2}}=689-254.7325 c 2 = 434.2675 {\displaystyle c^{2}=434.2675} c^{{2}}=434.2675 Take the square root of both sides of the equation. This will give you the missing side length: c 2 = 434.2675 {\displaystyle {\sqrt {c^{2}}}={\sqrt {434.2675}}} {\sqrt {c^{{2}}}}={\sqrt {434.2675}} c = 20.8391 {\displaystyle c=20.8391} c=20.8391So, the missing side length is 20.8391 cm long.
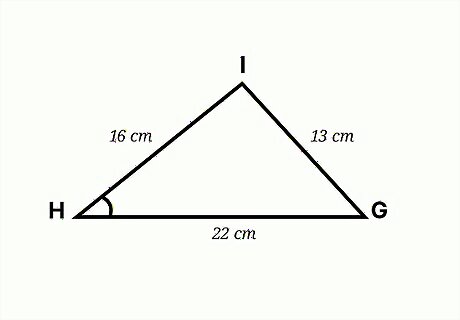
Find angle H in the triangle GHI. The two sides adjacent to angle H are 22 and 16 cm long. The side opposite angle H is 13 centimeter (5.1 in) long. Since you know all three side lengths, you can use the cosine rule. Set up the formula: c 2 = a 2 + b 2 − 2 a b cos C {\displaystyle c^{2}=a^{2}+b^{2}-2ab\cos {C}} c^{{2}}=a^{{2}}+b^{{2}}-2ab\cos {C}. The side opposite the missing angle is c {\displaystyle c} c. Plug all of the values into the formula: 13 2 = 22 2 + 16 2 − 2 ( 22 ) ( 16 ) cos C {\displaystyle 13^{2}=22^{2}+16^{2}-2(22)(16)\cos {C}} 13^{{2}}=22^{{2}}+16^{{2}}-2(22)(16)\cos {C}. Use the order of operations to simplify the expression: 13 2 = 22 2 + 16 2 − 704 cos C {\displaystyle 13^{2}=22^{2}+16^{2}-704\cos {C}} 13^{{2}}=22^{{2}}+16^{{2}}-704\cos {C} 13 2 = 484 + 256 − 704 cos C {\displaystyle 13^{2}=484+256-704\cos {C}} 13^{{2}}=484+256-704\cos {C} 169 = 484 + 256 − 704 cos C {\displaystyle 169=484+256-704\cos {C}} 169=484+256-704\cos {C} 169 = 740 − 704 cos C {\displaystyle 169=740-704\cos {C}} 169=740-704\cos {C} Isolate the cosine: 169 − 740 = 740 − 740 − 704 cos C {\displaystyle 169-740=740-740-704\cos {C}} 169-740=740-740-704\cos {C} − 571 = − 704 cos C {\displaystyle -571=-704\cos {C}} -571=-704\cos {C} − 571 − 704 = − 704 cos C − 704 {\displaystyle {\frac {-571}{-704}}={\frac {-704\cos {C}}{-704}}} {\frac {-571}{-704}}={\frac {-704\cos {C}}{-704}} 0.8111 = cos C {\displaystyle 0.8111=\cos {C}} 0.8111=\cos {C} Find the inverse cosine. This will give you the missing angle: 0.8111 = cos C {\displaystyle 0.8111=\cos {C}} 0.8111=\cos {C} 35.7985 = C O S − 1 {\displaystyle 35.7985=COS^{-1}} 35.7985=COS^{{-1}}.So, angle H is about 35.7985 degrees.
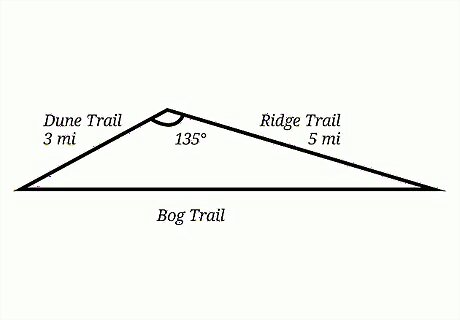
Find the missing trail length. Dune, Ridge, and Bog Trail form a triangle. Dune Trail is 3 miles long. Ridge Trail is 5 miles long. Dune Trail and Ridge Trail meet on their north ends at a 135 degree angle. Bog Trail connects the other two ends of the trails. How long is Bog Trail? The trails form a triangle, and you are asked to find a missing trail length, which is like the side of a triangle. Since you know the length of the other two trails, and you know they meet at 135 degree angle, you can use the cosine rule. Set up the formula: c 2 = a 2 + b 2 − 2 a b cos C {\displaystyle c^{2}=a^{2}+b^{2}-2ab\cos {C}} c^{{2}}=a^{{2}}+b^{{2}}-2ab\cos {C}. The missing side length (Bog Trail) is c {\displaystyle c} c. Plug the other values into the formula: c 2 = 3 2 + 5 2 − 2 ( 3 ) ( 5 ) cos 135 {\displaystyle c^{2}=3^{2}+5^{2}-2(3)(5)\cos {135}} c^{{2}}=3^{{2}}+5^{{2}}-2(3)(5)\cos {135}. Use the order of operations to find c 2 {\displaystyle c^{2}} c^{{2}}: c 2 = 3 2 + 5 2 − 2 ( 3 ) ( 5 ) cos 135 {\displaystyle c^{2}=3^{2}+5^{2}-2(3)(5)\cos {135}} c^{{2}}=3^{{2}}+5^{{2}}-2(3)(5)\cos {135} c 2 = 3 2 + 5 2 − 2 ( 3 ) ( 5 ) ( − 0.7071 ) {\displaystyle c^{2}=3^{2}+5^{2}-2(3)(5)(-0.7071)} c^{{2}}=3^{{2}}+5^{{2}}-2(3)(5)(-0.7071) c 2 = 3 2 + 5 2 − ( − 21.2132 ) {\displaystyle c^{2}=3^{2}+5^{2}-(-21.2132)} c^{{2}}=3^{{2}}+5^{{2}}-(-21.2132) c 2 = 9 + 25 + 21.2132 {\displaystyle c^{2}=9+25+21.2132} c^{{2}}=9+25+21.2132 c 2 = 55.2132 {\displaystyle c^{2}=55.2132} c^{{2}}=55.2132 Take the square root of both sides of the equation. This will give you the missing side length: c 2 = 55.2132 {\displaystyle {\sqrt {c^{2}}}={\sqrt {55.2132}}} {\sqrt {c^{{2}}}}={\sqrt {55.2132}} c = 7.4306 {\displaystyle c=7.4306} c=7.4306So, Bog Trail is about 7.4306 miles long.

















Comments
0 comment